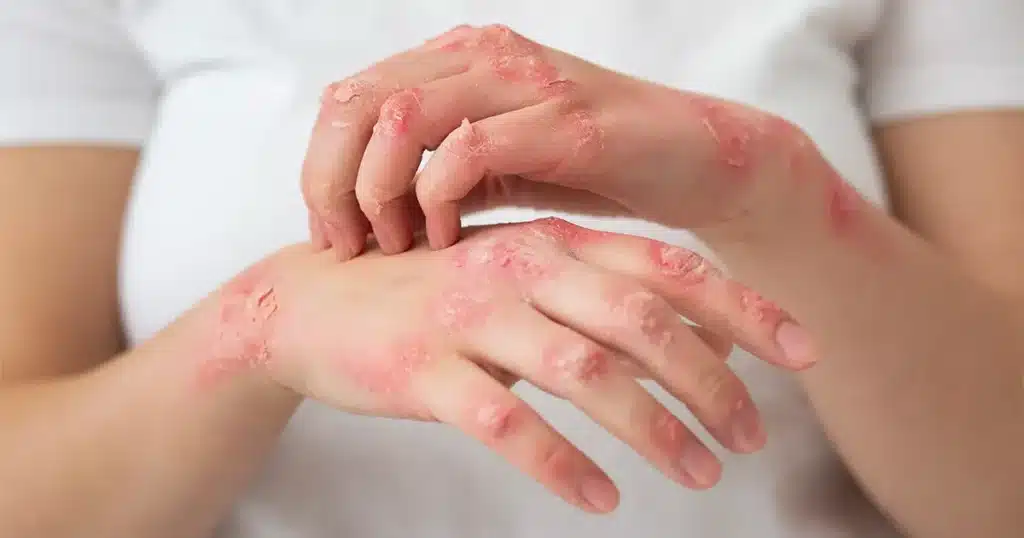
Skin Infections are common conditions caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invading the skin, leading to inflammation, pain, and discomfort. These infections can range from mild irritations to severe conditions affecting deeper tissues and overall health.
Early recognition of symptoms and timely medical care can prevent complications and improve recovery. Altus Emergency Centers offers emergency rooms in Lumberton, Lake Jackson, and Waxahachie, providing expert evaluation and treatment for skin infections, especially when symptoms worsen rapidly or complications arise.
What Are Skin Infections
Skin infections occur when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites invade the skin and overcome the body’s natural defenses. These infections range from superficial irritations like athlete’s foot to deeper, more serious infections such as cellulitis or abscesses. A review of outpatient dermatology data indicates that bacterial, viral, and fungal skin infections represent a significant clinical burden, with various pathogens contributing to different infection types and outcomes.
Symptoms Of Skin Infection
- Redness: The skin may appear red and inflamed as a sign of infection.
- Swelling: Infected areas can swell due to the immune response.
- Pain Or Tenderness: Affected skin often feels painful or sensitive to touch.
- Warmth: The area may feel warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Pus Or Discharge: Bacterial infections may produce pus or fluid.
Types Of Skin Infections
Skin infections differ depending on the pathogen involved and the depth of tissue affected. Recognizing the type of infection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further complications. Common categories of skin infections include:
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Conditions like cellulitis, impetigo, and abscesses caused by bacteria entering through cuts or abrasions.
- Fungal Skin Infections: Infections such as athlete’s foot or ringworm caused by fungi thriving in warm, moist areas.
- Viral Skin Infections: Viruses like herpes simplex or shingles cause painful blisters and lesions.
- Parasitic Skin Infections: Organisms such as mites or lice cause infestations like scabies or pediculosis.
What Causes Skin Infections
Skin infections occur when the skin’s protective barrier is compromised or when environmental or biological factors allow pathogens to invade. Small cuts, insect bites, excessive moisture, or chronic conditions like diabetes can increase susceptibility. Individuals with weakened immune systems or compromised skin are at higher risk.
Bacterial Causes
Bacterial skin infections occur when bacteria such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus enter through breaks in the skin. They often result in redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Without prompt treatment, these infections may progress to abscess formation or systemic spread. Early intervention with appropriate antibiotics prevents complications and speeds recovery.
Fungal Causes
Fungal infections develop when dermatophytes or yeasts invade the skin, thriving in warm, moist areas such as feet or skin folds. Symptoms include itching, scaling, and discoloration. Timely antifungal treatment and good hygiene prevent worsening and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Viral Causes
Viral infections such as herpes simplex or shingles affect skin cells and nerve endings, causing blisters, redness, and pain. They may recur, especially with immune suppression or stress. Early antiviral therapy reduces symptom severity, shortens recovery time, and prevents complications.
Parasitic Causes
Parasitic infections like scabies or lice occur when organisms burrow into the skin or live on hair and skin surfaces. These infections cause intense itching and irritation and can spread among close contacts. Effective treatment eradicates the parasite and prevents reinfestation.
Diagnosis For Skin Infections
Diagnosing skin infections involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests if necessary. Providers assess the affected area, severity, and patient symptoms. Tests like skin cultures or biopsies identify the specific pathogen, guiding precise treatment to improve outcomes.
- Physical Examination: Inspect the affected area for signs of infection and severity.
- Skin Culture: Samples may be analyzed to identify the microorganism.
- Microscopic Tests: Used for fungal or parasitic infections to confirm diagnosis.
- Blood Tests: Evaluate systemic involvement in severe infections.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI may be used if a deeper tissue infection is suspected.
When To Seek Emergency Care For Skin Infections
Severe or rapidly worsening skin infections require urgent medical attention. Complications such as sepsis or necrotizing infections can develop quickly, making early intervention critical.
- Rapidly Spreading Redness Or Swelling: May indicate aggressive infection.
- High Fever Or Chills: Suggests systemic involvement.
- Severe Pain Or Pus Discharge: Indicates serious infection.
- Blackened Skin Or Extreme Tenderness: May signal necrotizing infection.
- Confusion Or Weakness: Could indicate sepsis.
Contact Altus Emergency Centers immediately if any of these signs appear for expert emergency care in Lumberton, Lake Jackson, or Waxahachie.
How To Treat Skin Infection
Treatment for skin infections focuses on controlling the infection, reducing symptoms, and preventing complications. Most cases are managed with medications, proper wound care, and supportive measures. Prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider ensures effective therapy and minimizes the risk of recurrence or severe outcomes.
- Medications: Antibiotics, antifungals, or antivirals may be prescribed depending on the infection. Most doctors recommend completing the full course as directed.
- Wound Care: Keep the infected area clean and covered to prevent further contamination.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce discomfort.
- Hygiene Measures: Regular cleansing of affected areas, handwashing, and avoiding sharing personal items reduce the risk of spread.
- Monitoring: Watch for worsening symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, or fever, which may require urgent medical attention.
- Follow-Up Care: In some cases, follow-up visits ensure the infection has resolved and prevent complications.
Tips On How To Prevent Skin Infections
Maintaining healthy skin and hygiene is essential to prevent infections. Protecting minor wounds, keeping skin dry, and avoiding prolonged moisture exposure reduce risk. Those with chronic conditions should monitor their skin and consult healthcare providers as needed.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular cleansing removes pathogens.
- Protect Skin From Injury: Cover cuts, scratches, and abrasions.
- Keep Skin Dry And Clean: Moisture promotes fungal and bacterial growth.
- Monitor Chronic Conditions: Diabetes or immune compromise increases risk.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Towels, razors, and clothing can transmit infection.
- Seek Prompt Care: Early evaluation prevents worsening or complications.
Expert Emergency Care For Skin Infections
Skin infections can worsen quickly, especially in individuals with chronic conditions or weakened immune systems. At Altus Emergency Centers, our experienced medical team is ready to provide prompt evaluation and treatment, ensuring that serious infections receive the urgent care they need. Early intervention can prevent complications and support a faster, safer recovery.
Our emergency rooms are fully equipped to handle all types of skin infections, from mild irritations to severe or rapidly spreading cases. With comprehensive emergency care, Altus Emergency Centers offers accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and continuous monitoring, helping patients recover comfortably while reducing the risk of long-term complications.